New NASA Nuclear Rocket Plan Aims to Get to Mars in Just 45 Days : ScienceAlert
We live in an era of renewed space exploration, where multiple agencies are planning to send astronauts to the Moon in the coming years. This will be followed in the next decade with crewed missions to Mars by NASA and China, who may be joined by other nations before long.
These and other missions that will take astronauts beyond Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and the Earth-Moon system require new technologies, ranging from life support and radiation shielding to power and propulsion.
And when it comes to the latter, Nuclear Thermal and Nuclear Electric Propulsion (NTP/NEP) is a top contender!
NASA and the Soviet space program spent decades researching nuclear propulsion during the Space Race.
A few years ago, NASA reignited its nuclear program for the purpose of developing bimodal nuclear propulsion – a two-part system consisting of an NTP and NEP element – that could enable transits to Mars in 100 days.
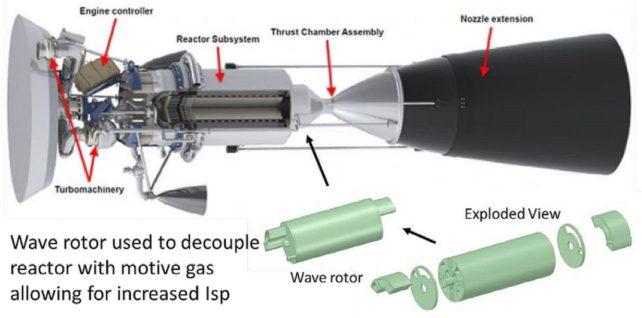
As part of the NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) program for 2023, NASA selected a nuclear concept for Phase I development. This new class of bimodal nuclear propulsion system uses a “wave rotor topping cycle” and could reduce transit times to Mars to just 45 days.
The proposal, titled “Bimodal NTP/NEP with a Wave Rotor Topping Cycle,” was put forward by Prof. Ryan Gosse, the Hypersonics Program Area Lead at the University of Florida and a member of the Florida Applied Research in Engineering (FLARE) team.
Gosse’s proposal is one of 14 selected by the NAIC this year for Phase I development, which includes a US$12,500 grant to assist in maturing the technology and methods involved. Other proposals included innovative sensors, instruments, manufacturing techniques, power systems, and more.
frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” allowfullscreen
Nuclear propulsion essentially comes down to two concepts, both of which rely on technologies that have been thoroughly tested and validated.
For Nuclear-Thermal Propulsion (NTP), the cycle consists of a nuclear reactor heating liquid hydrogen (LH2) propellant, turning it into ionized hydrogen gas (plasma) that is then channeled through nozzles to generate thrust.
Several attempts have been made to build a test this propulsion system, including Project Rover, a collaborative effort between the US Air Force and the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) that launched in 1955.
In 1959, NASA took over from the USAF, and the program entered a new phase dedicated to spaceflight applications. This eventually led to the Nuclear Engine for Rocket Vehicle Application (NERVA), a solid-core nuclear reactor that was successfully tested.
With the closing of the Apollo Era in 1973, the program’s funding was drastically reduced, leading to its cancellation before any flight tests could be conducted. Meanwhile, the Soviets developed their own NTP concept (RD-0410) between 1965 and 1980 and conducted a single ground test before the program’s cancellation.
Nuclear-Electric Propulsion (NEP), on…
Read More: New NASA Nuclear Rocket Plan Aims to Get to Mars in Just 45 Days : ScienceAlert
