Why ‘quantitative tightening’ is the wild card that could sink the stock market
Quantitative monetary easing is credited for juicing stock market returns and boosting other speculative asset values by flooding markets with liquidity as the Federal Reserve snapped up trillions of dollars in bonds during both the 2008 financial crisis and the 2020 coronavirus pandemic in particular. Investors and policy makers may be underestimating what happens as the tide goes out.
“I don’t know if the Fed or anybody else truly understands the impact of QT just yet,” said Aidan Garrib, head of global macro strategy and research at Montreal-based PGM Global, in a phone interview.
The Fed, in fact, began slowly shrinking its balance sheet — a process known as quantitative tightening, or QT — earlier this year. Now it’s accelerating the process, as planned, and it’s making some market watchers nervous.
A lack of historical experience around the process is raising the uncertainty level. Meanwhile, research that increasingly credits quantitative easing, or QE, with giving asset prices a lift logically points to the potential for QT to do the opposite.
Since 2010, QE has explained about 50% of the movement in market price-to-earnings multiples, said Savita Subramanian, equity and quant strategist at Bank of America, in an Aug. 15 research note (see chart below).
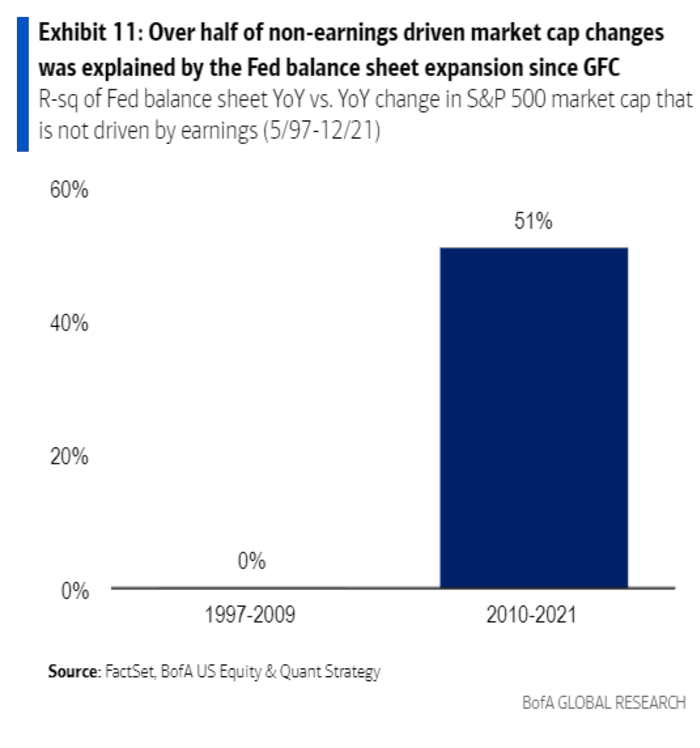
BofA U.S. Equity & Quant Strategy
“Based on the strong linear relationship between QE and S&P 500 returns from 2010 to 2019, QT through 2023 would translate into a 7 percentage-point drop in the S&P 500 from here,” she wrote.
Archive: How much of the stock market’s rise is due to QE? Here’s an estimate
In quantitative easing, a central bank creates credit that’s used to buy securities on the open market. Purchases of long-dated bonds are intended to drive down yields, which is seen enhancing appetite for risky assets as investors look elsewhere for higher returns. QE creates new reserves on bank balance sheets. The added cushion gives banks, which must hold reserves in line with regulations, more room to lend or to finance trading activity by hedge funds and other financial market participants, further enhancing market liquidity.
The way to think about the relationship between QE and equities is to note that as central banks undertake QE, it raises forward earnings expectations. That, in turn, lowers the equity risk premium, which is the extra return investors demand to hold risky equities over safe Treasurys, noted PGM Global’s Garrib. Investors are willing to venture further out on the risk curve, he said, which explains the surge in earnings-free “dream stocks” and other highly speculative assets amid the QE flood as the economy and stock market recovered from the pandemic in 2021.
However, with the economy recovering and inflation rising the Fed…
Read More: Why ‘quantitative tightening’ is the wild card that could sink the stock market
