Strange Footprints From Laetoli, Tanzania, Are From Early Humans
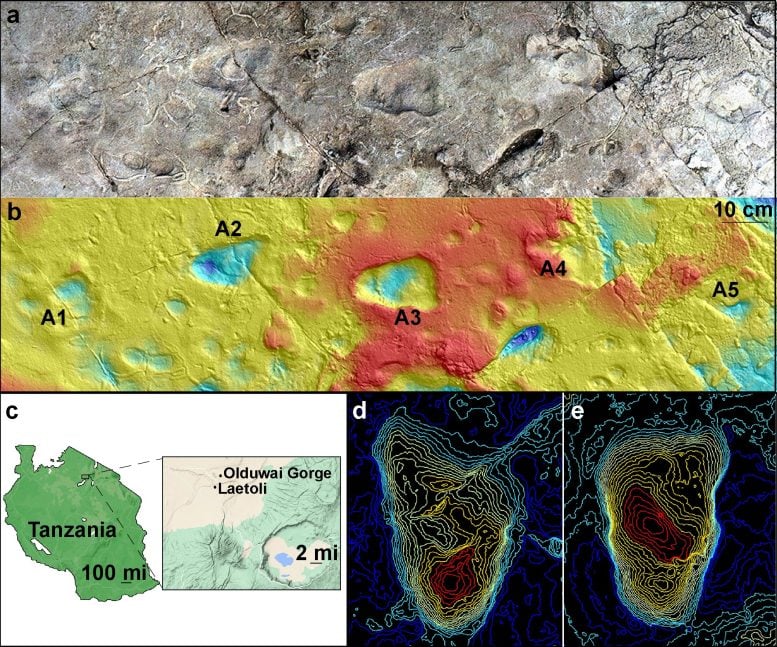
Model of Laetoli Site A using photogrammetry showing five hominin footprints (a); and corresponding contour map of the site at Laetoli, Tanzania, generated from a 3D surface scan (b); map showing Laetoli, which is located within the Ngorongoro Conservation Area in northern Tanzania, south of Olduvai Gorge (c); topographical maps of A2 footprint (d) and A3 footprint (e). Credit: Images (a) and (b) by Austin C. Hill and Catherine Miller. Image (c): Illustration using GoogleMaps by Ellison McNutt. Images (d) and (e) by Stephen Gaughan and James Adams
Findings provide conclusive evidence that multiple species of hominins co-existed on the landscape.
The oldest unequivocal evidence of upright walking in the human lineage are footprints discovered at Laetoli, Tanzania in 1978, by paleontologist Mary Leakey and her team. The bipedal trackways date to 3.7 million years ago. Another set of mysterious footprints was partially excavated at nearby Site A in 1976 but dismissed as possibly being made by a bear. A recent re-excavation of the Site A footprints at Laetoli and a detailed comparative analysis reveal that the footprints were made by an early human— a bipedal hominin, according to a new study reported in Nature.
“Given the increasing evidence for locomotor and species diversity in the hominin fossil record over the past 30 years, these unusual prints deserved another look,” says lead author Ellison McNutt, an assistant professor of instruction at the Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine at Ohio University. She started the work as a graduate student in Ecology, Evolution, Environment, and Society at Dartmouth College, where she focused on the biomechanics of walking in early humans and utilized comparative anatomy, including that of bears, to understand how the heel bone contacts the ground (a foot position called “plantigrady”).
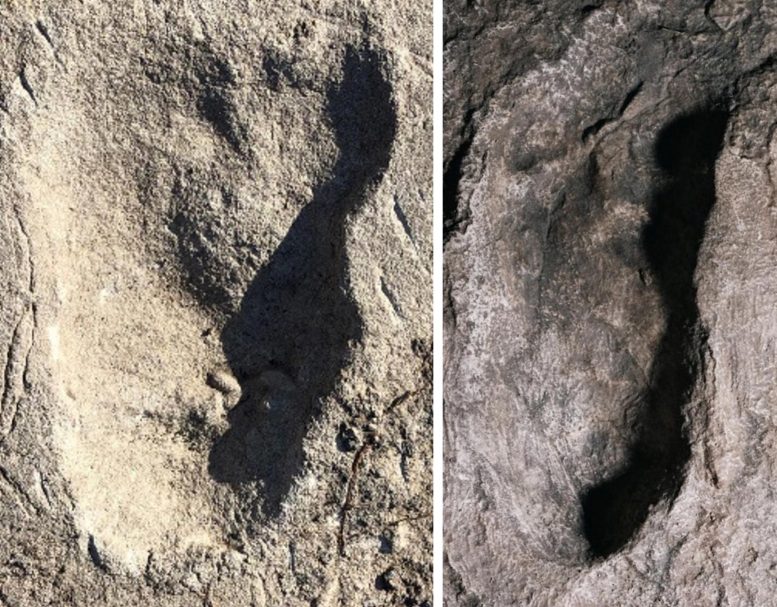

Image of Laetoli A3 footprint (on left) and image of a cast of Laetoli G1 footprint (on right). Analysis shows similarities in length of Laetoli A3 and G footprints but differences in forefoot width with the former being wider. Credit: Image on left by Jeremy DeSilva and on right by Eli Burakian/Dartmouth
McNutt was fascinated by the bipedal (upright walking) footprints at Laetoli Site A. Laetoli is famous for its impressive trackway of hominin footprints at Sites G and S, which are generally accepted as Australopithecus afarensis—the species of the famous partial skeleton “Lucy.” But because the footprints at Site A were so different, some researchers thought they were made by a young bear walking upright on its hind legs.
To determine the maker of the Site A footprints, in June 2019, an international research team led by co-author Charles Musiba, an associate professor of anthropology at University of Colorado Denver, went to Laetoli, where they re-excavated and fully cleaned the five, consecutive footprints. They identified evidence that the fossil footprints were made by a hominin—including a large impression for the heel and the big toe. The footprints were measured, photographed and 3D-scanned.
The researchers compared the Laetoli Site A tracks to the footprints of black bears (Ursus…
Read More: Strange Footprints From Laetoli, Tanzania, Are From Early Humans
